How to find out the Autonomous system on the IP and how to find out all the Autonomous System IPs
What is an Autonomous System (AS)
To understand what the concept of ‘Autonomous Systems’ is for, you need to have an idea about the routing of data on the Internet.
The structure of the network of an Internet provider or a large organization can be simply represented as a set of local networks that are connected to a router connected to routers of other Internet providers and organizations to exchange data with the Global Network (Internet). By the way, a group of routers of one company is in fact an Autonomous System.
Suppose this is understandable, but why did they have to assign numbers to everyone?
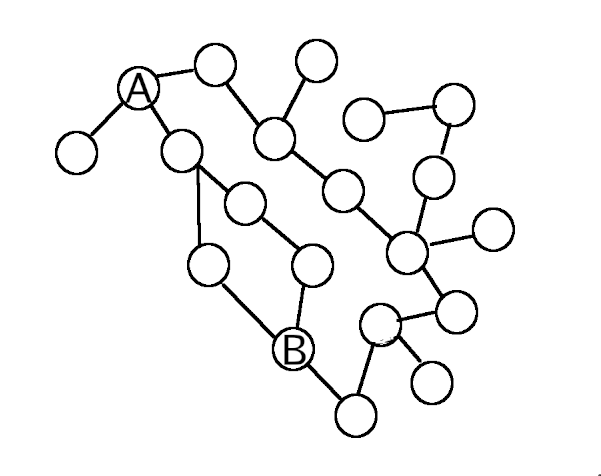
If a packet is intended for a node located in the global network, then when it reaches the router, then since the router can be connected to several other routers of other Autonomous Systems at once, the question arises – where to send this packet? Suppose that router A needs to forward a packet to router B:
How to find out which node to send the package to? How will the second node choose the next one to send? What will the third node do? Even in my simple picture, it is clear that there are long routes to the same point, and there are even dead ends.
These questions are answered by routing protocols, for example, Border Gateway Protocol. Thanks to them the router ‘knows’ the best (not necessarily the shortest, there are several evaluation criteria) path from point A to point B. And such protocols operate with the terms ‘Autonomous System’. That is, to put it simply, such protocols build routes along the nodes of an autonomous system, taking into account which nodes are connected to this router, which are connected to the next one, and so on.
So, the Autonomous System (AS) is a group of gateways (routers) that are under the same administrative control, that is, belong to the same organization.
Such organizations can be:
- Internet service providers
- Hosting providers
- Search engines
- Organizations providing network services
- Other
Autonomous System Number (ASN) is a numeric identifier for networks participating in the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). BGP is a protocol in which routes are defined for transmitting packets around the world. Without BGP, Internet traffic could not leave the local networks.
The ASN defines an Internet protocol block group for versions 4 or 6.
Why bother trying to determine ASN by IP?
When collecting information using ASN, you can get some additional data:
- determine that different IPs belong to the same organization (if for each of them the same ASN means the organization is the same)
- for ASN, you can get a brief description of the organization, sometimes some contact details and other information (something like whois)
- find out all ranges of IP addresses of organizations
Autonomous system lookup using command line in Linux
1. How to find out the Autonomous System using the dig command
Using such a construction (replace 185.117.153.79 in it with the IP of interest), you can find out the Autonomous System number, the range to which the IP address belongs, the country and the allocation date:
dig $(dig -x 185.117.153.79 | grep PTR | tail -n 1 | grep -Eo '[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}').origin.asn.cymru.com TXT +short
Example output:
"48666 | 185.117.152.0/22 | RU | ripencc | 2015-09-16"
It is this way (DNS query *.origin.asn.cymru.com) to find out AS is used in the mtr command (it was considered in the article about tracing).
In the article “Autonomous system lookup using command line in Linux”, it was suggested to make a function:
function asn() { dig $(dig -x $1 | grep PTR | tail -n 1 | grep -Eo '[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}').origin.asn.cymru.com TXT +short }
You can put it in the ~/.bashrc. Then right in the console you can use the function:
asn 185.117.153.79
2. Getting AS from cymru.com database
The cymru.com database supports requests using the whois protocol (replace the 185.117.153.79 command with the IP address of interest):
whois -h whois.cymru.com -- '-v 185.117.153.79'
In the previous command, two dashes in a row tell the command that subsequent input is not its options. This is done so that the whois command does not treat -v as its option.
Example output:
AS | IP | BGP Prefix | CC | Registry | Allocated | AS Name 48666 | 185.117.153.79 | 185.117.152.0/22 | RU | ripencc | 2015-09-16 | AS-MAROSNET Moscow, Russia, RU
3. Getting the AS from the whois.radb.net database
And I found this method in the traceroute program – when it needs to know the Autonomous System number, it accesses the database whois.radb.net. Request example:
whois -h whois.radb.net 185.117.153.79
Example output:
route: 185.117.152.0/22 descr: MAROSNET Telecommunication Company Network descr: Moscow, Russia descr: http://www.marosnet.ru/ origin: AS48666 mnt-by: MAROSNET-MNT created: 2015-09-16T10:53:39Z last-modified: 2015-09-16T10:53:39Z source: RIPE remarks: **************************** remarks: * THIS OBJECT IS MODIFIED remarks: * Please note that all data that is generally regarded as personal remarks: * data has been removed from this object. remarks: * To view the original object, please query the RIPE Database at: remarks: * http://www.ripe.net/whois remarks: ****************************
If you only need an AS number, you can run it like this:
whois -h whois.radb.net 185.117.153.79 | grep '^origin'
4. Using the hackertarget.com API
The hackertarget.com site contains a database and provides a command-line-friendly API: https://api.hackertarget.com/aslookup/?q=185.117.153.79
To get data on the command line:
curl https://api.hackertarget.com/aslookup/?q=185.117.153.79
Example output:
"185.117.153.79","48666","185.117.152.0/22","AS-MAROSNET Moscow, Russia, RU"
5. How to find out the autonomous system number using WHOIS
By default, a request from the whois command is addressed to the whois.ripe.net database. It also shows the origin field for some IP addresses:
whois 185.117.153.79 | grep 'origin'
Another option (the output of the command will be limited to the route section):
whois -T route 185.117.153.79
Example output (comments are removed):
route: 185.117.152.0/22 descr: MAROSNET Telecommunication Company Network descr: Moscow, Russia descr: http://www.marosnet.ru/ origin: AS48666 mnt-by: MAROSNET-MNT created: 2015-09-16T10:53:39Z last-modified: 2015-09-16T10:53:39Z source: RIPE
How to find out information about the Autonomous System
1. Obtaining Autonomous System information from the whois.cymru.com database:
whois -h whois.cymru.com -- '-v AS48666'
Example output:
AS | CC | Registry | Allocated | AS Name 48666 | RU | ripencc | 2008-12-29 | AS-MAROSNET Moscow, Russia, RU
2. Getting information about the Autonomous system from the database whois.radb.net:
The whois.radb.net database contains additional technical information about the Autonomous System:
whois -h whois.radb.net AS48666
The information about some autonomous systems:
whois -h 198.108.0.18 AS3
contains links to other records in the database
tech-c: See MAINT-AS3
which can also be viewed:
whois -h 198.108.0.18 MAINT-AS3
3. Autonomous Systems in WHOIS
The usual whois command can also display information about AS by their number:
whois AS48666
How to find out all IP ranges of the Autonomous System
By AS number, you can find the IP address ranges of the Internet provider, search engine, hosting providers, any other organization that has been allocated IP.
1. Getting the Autonomous System IP from radb.net
The following command displays information about the routes of this AS:
whois -h whois.radb.net -- '-i origin AS48666'
More compressed output:
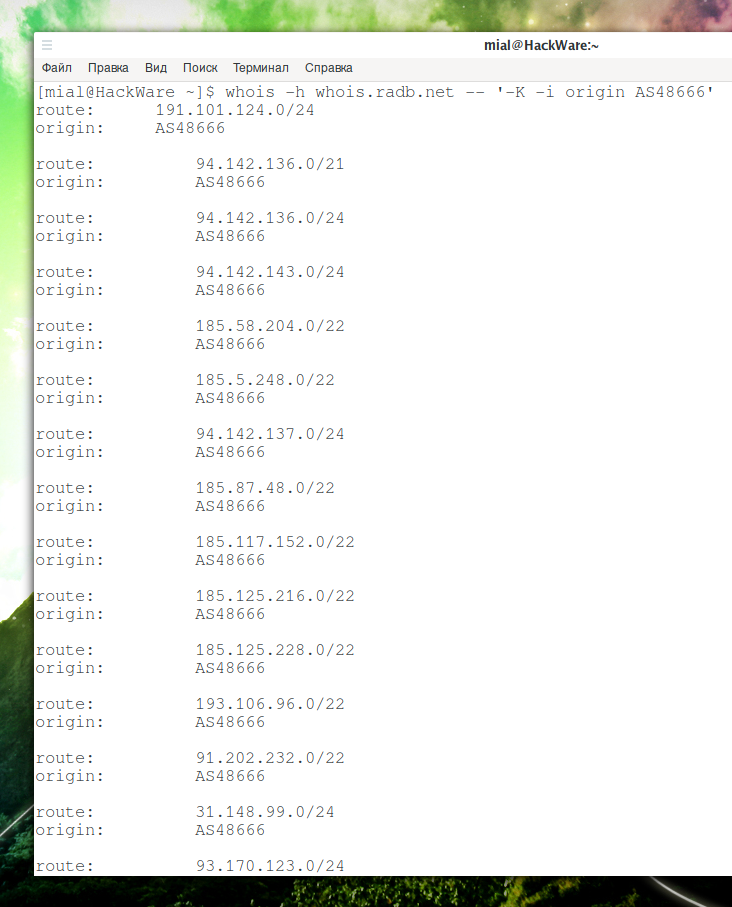
whois -h whois.radb.net -- '-K -i origin AS48666'
Filtering only the necessary lines:
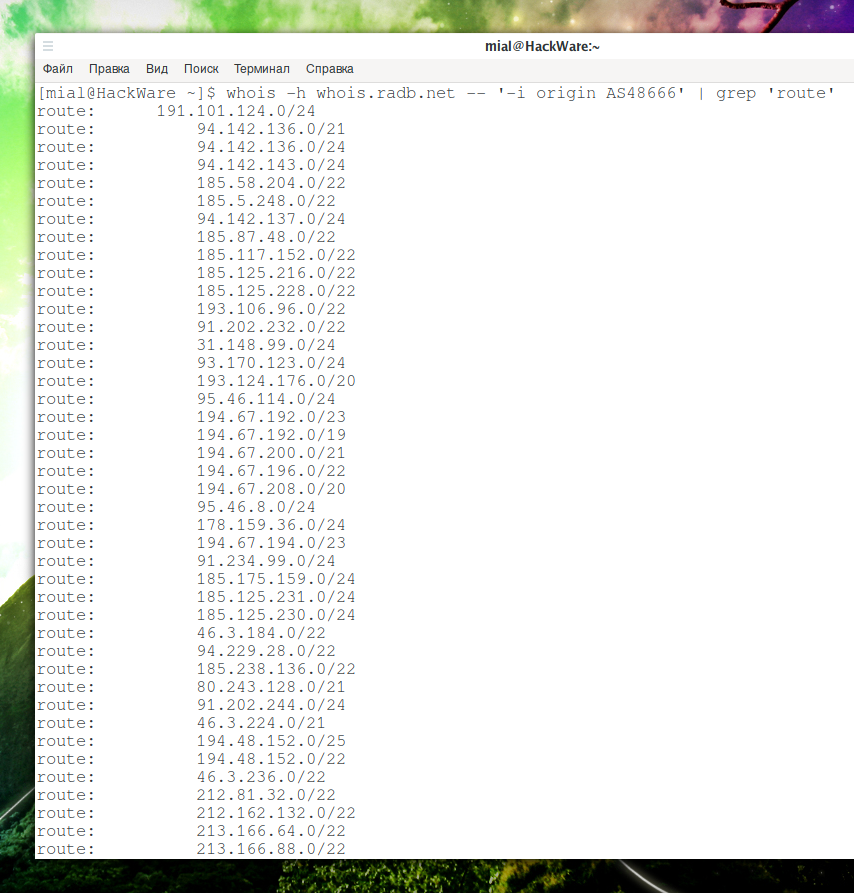
whois -h whois.radb.net -- '-i origin AS48666' | grep 'route'
But the lists of ranges obtained in this way require additional attention, since some of them include other ranges from the same list.
2. IP ranges from hackertarget.com database
Using the hackertarget.com API, you can get the IP ranges of organizations: https://api.hackertarget.com/aslookup/?q=AS48666
Including the command line:
curl https://api.hackertarget.com/aslookup/?q=AS48666
Conclusion
Please note that the ranges shown may contain the same IP addresses. For my service to find IP addresses and ranges of any ISP (there are not only providers – any AS), I used a similar method of getting ranges at the beginning, but because of this lack I wrote my own script for extracting data from the database. Therefore, on the service by reference, the resulting ranges should not contain the same IP.
Related articles:
- How to find out if a site is behind CloudFlare or not (82.4%)
- Revealing the perimeter (CASE) (72.4%)
- IP addresses databases of organizations and geographical places (continents, countries, provinces and cities) (67.4%)
- Utilities for information gathering, OSINT and network analysis in Windows and Linux (65.2%)
- FinalRecon: a simple and fast tool to gather information about web sites, works on Windows (61.1%)
- Dissection of the scammer site (case) (RANDOM - 52.5%)