Generation and modification of word lists according to the given rules
To generate word lists, there are very flexible maskprocessor and Crunch programs. They can create any word lists based on complex rules or specific patterns.
- phone numbers
- birth dates
- 8-character passwords that contain letters and numbers
- passwords starting with a specific word followed by a certain number of digits
- passwords in which the first two characters are capital letters, then comes 4 uppercase letters, then eight digits, then two hexadecimal characters
- etc.
You can come up with a huge amount of options, but somehow they come down to a description of which position which symbol should be.
If we take more abstract constructions, for example:
- password from names that ends with several numbers,
- a dictionary of popular words in which the characters “a” are replaced by “@”
- dictionary in which the case of some letters is changed
- expletives words in which a certain strings is placed before the word
- etc.
To perform such tasks, the Mentalist program was created. Mentalist is a graphical tool for custom wordlist generation. It utilizes common human paradigms for constructing passwords and can output the full wordlist as well as rules compatible with Hashcat and John the Ripper.
It knows how to build chains of actions – you can set any logic for processing ready dictionaries or modifying a given string. The program has a graphical user interface, and it also works on both Linux and Windows.
How to install mentalist
Installation is quite simple, regardless of whether you decide to use a compiled binary file or build from source codes.
Installation on Kali Linux
sudo apt install python3-setuptools python3-tk git clone https://github.com/sc0tfree/mentalist cd mentalist/ sudo python3 setup.py install
Installation on Windows
Go to https://github.com/sc0tfree/mentalist/releases and download the latest version for Windows, that is, a file of the form Mentalist-v*-Win.zip. Unzip the archive and double-click the Mentalist.exe file.
How to use mentalist
To understand the work of Mentalist, you must consider the basic concepts of the program.
The Chain
Mentalist generates wordlists by linking together nodes, which form a chain. The first node in a chain is always the Base Words node. When the chain is processed, each Base Word passes to the next node in the chain, which might modify the word, leave it the same or create more variations of it. Finally, the results are written to an output file as either the full wordlist or rules to generate the equivalent list.
Nodes
There are 5 types of nodes. Each type has its own set of attributes, which can be added in any combination. A node's attributes determine its function. Furthermore, attributes within the same node are mutually exclusive from each other.
Some nodes may produce more than one output word for each input word. In such cases, only the set of unique output words for a Base Word is passed on to the next node. In other words, each node performs de-duplication on each base word.
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Base Words | Always the first node within the Mentalist chain. It provides the root words, which are to be processed by each node as they pass down the chain. |
| Case | Changes the case of letters within the word. Each attribute added to a Case node produces a different variation of the input word, except for the No Case Change attribute which passes through the original word. |
| Substitution | Replaces characters within the word. Like Case, each attribute added to a Substitution node produces another output word, subject to de-duplication. The No Substitution attribute gives the unmodified input word. |
| Append |
Append nodes add strings to the end of the input word. Most Append attributes produce many variations of the input word. For example, the Numbers: Small (0-100) attribute adds 101 output words for each input word.
|
| Prepend | Prepend nodes add strings to the beginning of the input word. Its attributes and functionality is otherwise identical to Append. |
Attributes
Each node has the ability to perform one or more actions on the input words. These actions are specified in each node's attributes. Attributes within the same node are mutually exclusive of each other and, as a consequence, a node can have no duplicate attributes.
Node Attributes
Base Words
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| No Words | Provides an empty string |
| Custom File… | User-specified custom wordlist file |
| Custom String… | User-specified custom string |
| English Dictionary |
English dictionary taken from the Unix words file
|
| Common Names | |
| Men | 1,000 most common mens' names in the US |
| Women | 1,000 most common womens' names in the US |
| Pets | 1,200 most common pets' names in the US |
| Other | |
| Slang & Expletives | Wordlist of US slang and expletives |
| Months & Seasons | Wordlist of months and seasons |
Case
| Attribute | Description | Input | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| No Case Change | Perform no action | TeSt | TeSt |
| Lowercase | |||
| Lowercase All | Make word all lowercase | TeSt | test |
| Lowercase First, Upper Rest | Make first character lowercase and the rest of the word uppercase | TeSt | tEST |
| Uppercase | |||
| Uppercase All | Make word all uppercase | TeSt | TEST |
| Uppercase First, Lower Rest | Make first character uppercase and the rest of the word lowercase | TeSt | Test |
| Toggle Nth… | Change the case of the Nth character | TeSt (N=2) | TESt |
Substitution
| Attribute | Description | Input | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| No Substitution… | Perform no action | test | test |
| Replace All Instances… | Replaces all instances of specified characters |
test ('t'→'+') |
+es+ |
| Replace First Instance… | Replace the first instance of specified characters |
test ('t'→'+') |
+est |
| Replace Last Instance… | Replace the last instance of specified characters |
test ('t'→'+') |
tes+ |
If a word does not match criteria for substitution, it will be output unchanged.
Note: Replace First Instance and Replace Last Instance are not compatible with Hashcat & John rules. If attempting to output rules using one of these attributes in your chain, Mentalist will ask if you would like to replace these attributes with the Replace All Instances, which is a supported rule.
Additional Substitution Options
One at a Time substitution will only substitute one specified character at a time.
All at Once substitution will substitute all characters at once.
| Option | Input | Substitutions | Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| One at a Time | apple |
'a'→'@' 'e'→'3' |
@pple appl3 |
| All at Once | apple |
'a'→'@' 'e'→'3' |
@ppl3 |
Append / Prepend
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| No Append / Prepend | Perform no action |
| Words | |
| Custom File… | User-specified custom wordlist file |
| Custom String… | User-specified custom string |
| English Dictionary |
English dictionary taken from the Unix words file
|
| Common Names | |
| Men | 1,000 most common mens' names in the US |
| Women | 1,000 most common womens' names in the US |
| Pets | 1,200 most common pets' names in the US |
| Other | |
| Slang & Expletives | Wordlist of US slang and expletives |
| Months & Seasons | Wordlist of months and seasons |
| Numbers | |
| User Defined… | User-specified numbers (From, To, 0-padding) |
| Small: 0-100 | Numbers ranging from 0 to 100 |
| Basic: 0-1000 | Numbers ranging from 0 to 1000 |
| Full: 0-10000 | Numbers ranging from 0 to 10000 |
| Years: 1950-2025 | Numbers ranging from 1950 to 2025 |
| Dates… | Dates: From Year, To Year, Format (e.g. mmddyy), Leading 0 |
| Special Characters… | Special characters (one at a time only) |
| Area Codes (US) | |
| By State | Area codes by state |
| By City | Area codes by city (largest 50 available) |
| Zip Codes (US) | |
| By State | Zip codes by state |
| By City | Zip codes by city (largest 50 available) |
Output
Full Wordlist
This option outputs the entire wordlist, as specified by the chain. The estimated number of words and filesize can be found in the top menu of Mentalist.
Hashcat/John Rules
For offline cracking, there are times where the full wordlist is too large to output as a whole. In this case, it makes sense to output to rules so that Hashcat or John can programmatically generate the full wordlist.
Note that the First and Last Substitution attributes are not compatible with Hashcat/John. When a chain contains these attributes, saving to Hashcat/John will warn that First or Last will be changed to All in the rules output.
Base Words Only
This output option allows you to output the base words into a single file to be used with your rules. This is useful if you have multiple sources of base words (multiple Base Word attributes).
Reuse Chains
Saving Chains
Mentalist is able to save chain files for future use. To save a chain file, go to Load/Save→Save Chain, which will then prompt you where you'd like to save the file. For organization, saved Mentalist chains should have the extension .mentalist, which is enforced in the application on most OSes.
Loading Chains
Mentalist is able to load chain files by clicking on Load/Save→Load Chain. If the chain file refers to a user-specified file that is not present on the current system, Mentalist will put a red box around that file attribute and will prevent processing. To fix this, click on the Fix... button next to the file and specify a local file in its place.
Examples of use Mentalist
1.
Suppose we need to create a dictionary based on an existing list of words in which 2 to 4 digits follow a word and in which all the letters “a” are replaced by “@” and the letters “s” are replaced by “$”.
Run the program:
mentalist
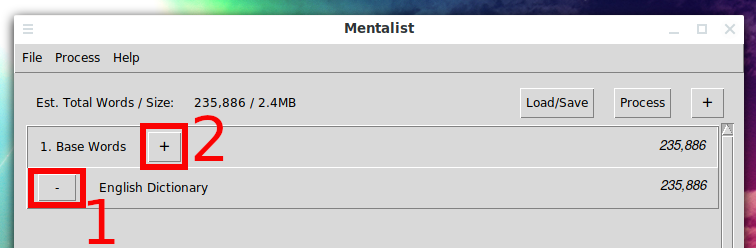
Please note that a list of English words is already selected by default. We delete it for this, click on the “-” sign.
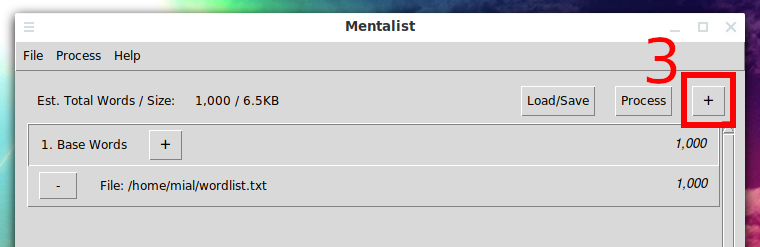
Then click the “+” sign next to “Base Word”, select “Custom File…” and specify the dictionary you want to change.
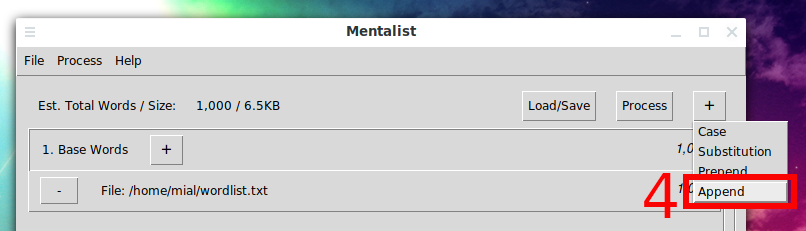
Then click on the “+” sign in the upper right corner and select “Append”.
Then click the “+” sign next to “Append”, then select “Numbers” and then “User Defined…”.
Then click on the “+” sign in the upper right corner and select “Substitution”.
Then click the “+” sign next to “Substitution”, then select “Replace All Instances…” and then “User Defined…”, put the necessary check-boxes and switch to “All at Once”.
Please note that if you select “One at a Time” instead of “All at Once”, then the first character will be replaced first and then the word will be sent further along the pipeline, then the second character will be replaced and the word will be sent again along the pipeline. That is, the “One at a Time” option increases the number of new words by a factor – in accordance with the number of replacements.
To save a new dictionary, click “Process”, then select “Full Wordlist”.
2.
Suppose now we need to create a dictionary based on female names in which the letters “a” are replaced by the symbol “@”. Moreover, it is necessary that both the original name and the name with the replacement of characters are preserved. Then after the name comes a dash. Then the date is inserted in the DDMMYYYY format.
Run the program:
mentalist
Please note that a list of English words is already selected by default. We delete it for this, click on the “-” sign.
Then click the “+” sign next to “Base Word”, select “Common Names”, then “Women”.
Then click on the “+” sign in the upper right corner and select “No Substitution…”.
Click the “+” sign next to “Substitution” again, then select “Replace All Instances…” and then “User Defined…”, put the necessary check-boxes and switch to “All at Once”.
Then click the “+” sign next to “Substitution”, then select “Replace All Instances…” and then “User Defined…”, put the necessary check-boxes and switch to “All at Once”.
Then click on the “+” sign in the upper right corner and select “Append”.
Then click the “+” sign next to “Append”, then select “Special Characters…” and put a check-boxes in front of the “-” symbol:
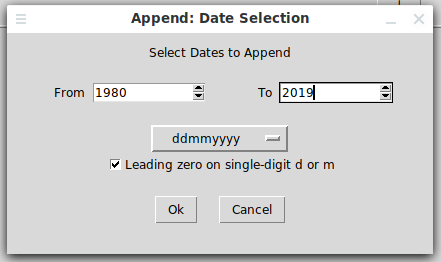
Now again press the “+” sign next to “Append”, then select “Numbers” and then “Dates…”. Set the desired range and format:
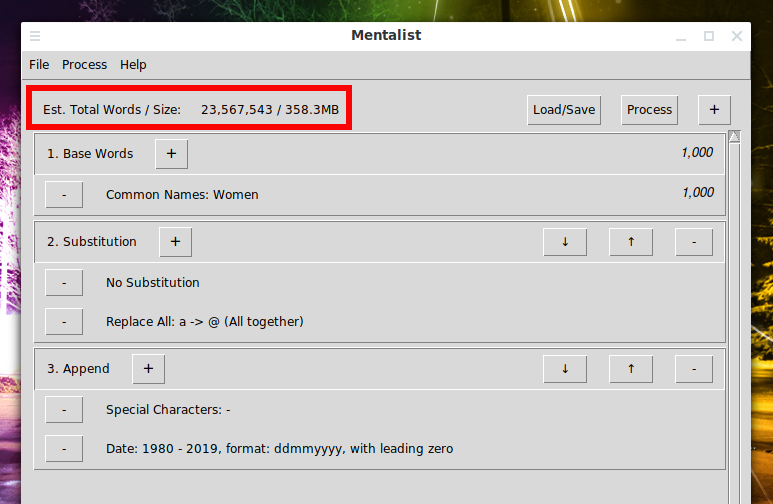
We get the following result, pay attention to the approximate number of words in the new dictionary and the size of the dictionary in megabytes:
To save a new dictionary, click “Process”, then select “Full Wordlist”.
Conclusion
So, Mentalist is a convenient and easy-to-use program for creating dictionaries according to more abstract rules than maskprocessor и Crunch. First of all, it is convenient for modifying existing dictionaries under specific conditions. However, it will not be able to replace maskprocessor and Crunch, since they are more flexible in creating dictionaries based on the rules for arranging characters in certain positions.
Related articles:
- How to generate candidate passwords that match password strength policies (filtering words with grep) (100%)
- Generation and modification of dictionaries according to the specified rules (100%)
- Programs for generating wordlists (100%)
- How to use .hcmask files in Hashcat for the most flexible character replacement (100%)
- Advanced wordlist generating techniques (94.6%)
- WiFi-autopwner 2: user manual and overview of new features (RANDOM - 5.4%)