What to select: Tor, VPN, or proxy?
In this article we will discuss the question: Is Tor better than VPN and proxy?
What is Tor
There are several different components and products in the name of which is the word “Tor”. To clearly understand what we're talking about, let's start by defining the terms.
Tor is a program that you can run on your computer to connect to the Tor network.
The Tor network is a multitude of volunteer computers that process requests to web sites and send back the response to the Tor user.
The Tor browser is a complex of programs whose main components are: Tor + Firefox browser + plugins and settings to increase anonymity.
What is Tor used for?
Tor can be used for various purposes:
- data encryption so that it cannot be analyzed by an Internet service provider or by unauthorized persons on your local network or when using open networks (example of the attack in the article ‘How to intercept and analyze traffic in open Wi-Fi’).
- hiding your IP address from the target website
- access blocked websites in your area
What to choose: Tor or VPN or proxy
If your goal is to encrypt the transmitted data so that your Internet service provider cannot analyze it, then Tor and your VPN, which you set up yourself, can do the job! I would not recommend using any third-party VPNs, since their owner can see all the transmitted traffic + client IP (that is, your IP address). If you use a third-party VPN service, then you are guaranteed to get an eavesdropper who, at a minimum, also knows your real IP address! If this is a paid VPN, then it is absolutely not suitable for anonymity, since the VPN service does not only know your IP and has access to all transmitted data, then it knows who you are by your payment details.
The self-configured OpenVPN allows you to encrypt the transmitted traffic and connect your devices into a virtual private network. You can also hide your real IP address and bypass site blocking. But for anonymity, this option is not suitable, because for the operation of OpenVPN you need to rent a VPS, for which you have to pay. Although if you use cryptocurrency or other anonymous methods for payment, OpenVPN will help you to be anonymous.
Using a single proxy has the same disadvantages as a VPN: the eavesdropper + proxy service knows your real IP address. An additional drawback in the absence of encryption is that your ISP can still analyze your traffic and even block access to websites.
The situation with IP concealment improves if a proxy chain is used, because (depending on the settings), each next proxy knows the IP address of the previous node (always) and the IP address of 1 node before the previous one (sometimes). If we consider that traffic is not encrypted at any stage, and a certain part of public proxies is just honeypots (intended for the exploitation of users), then the proxy option is not the best way to ensure anonymity.
What exactly Tor helps for
Of course, Tor also has its weaknesses. There are fewer of them, but you still need to clearly understand them.
Let's turn to the ‘comics’:
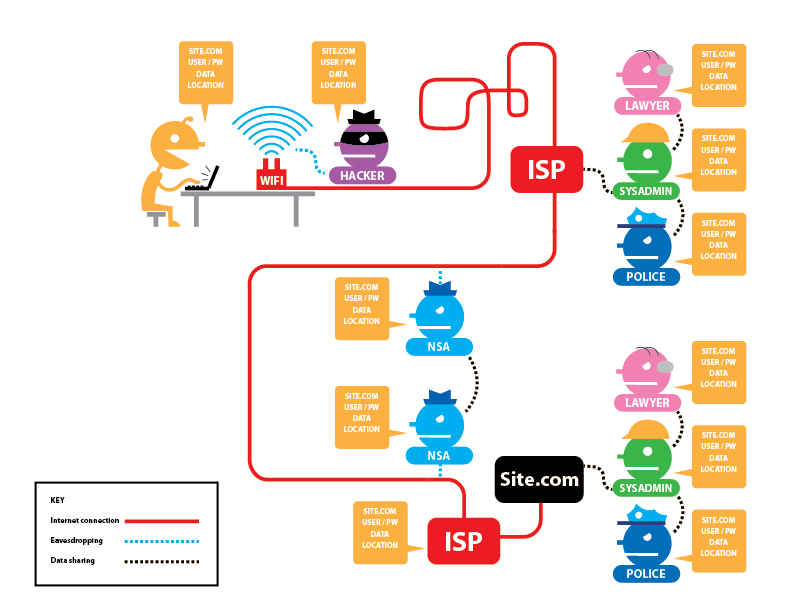
On this picture:
- the yellow man is the user (you)
- the lilac man is a hacker (in practice, it is not always present)
- ISP is an Internet service provider that shares information with the police and special authorities. Also, there are system administrators who also (potentially) have access to the transmitted data. Please note that 2 Internet providers are shown: for the user and for the website. Hosting usually acts as an ISP for a site, but this doesn’t change anything fundamentally: it may also be required to provide information to law enforcement agencies and system administrators work there too.
- NSA people – represent all the other ISPs through which data passes, as well as different trunk connections
The first figure shows what they can see if: 1). The website does not use HTTPS; 2) The user does not use Tor.
Legend:
- SITE.COM – the site you visit
- USER/PW – your username and password on this site
- DATA – data transmitted to this site (written comments, for example)
- LOCATION – your IP address
- TOR – is Tor used
As you can see from the first picture, everyone can see absolutely everything. It is also worth adding – not only to see, but also to modify in any way!
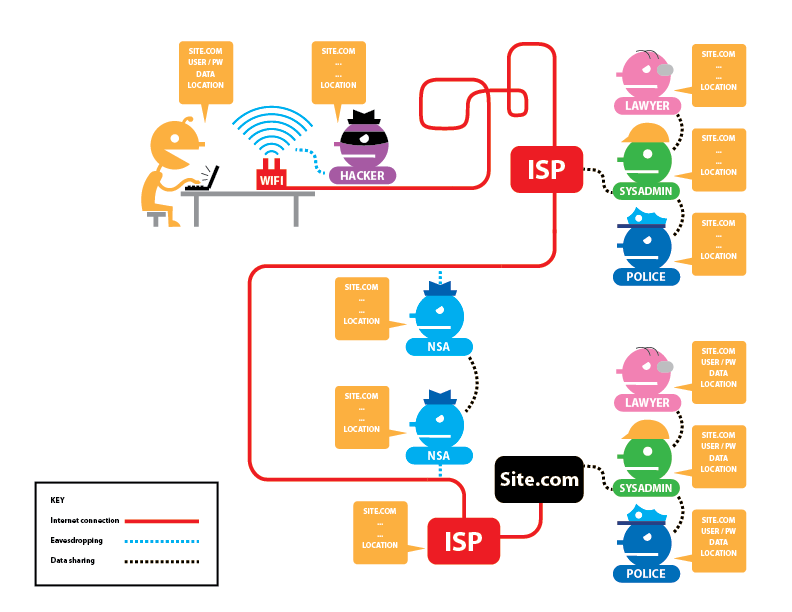
Let's look at an option when a website uses HTTPS – currently the vast majority of sites use this encryption:
As you can see, only information about which site is open and who exactly visited it is available to the eavesdropper. If a website (hosting) shares information with someone, then a complete set of data is available to them.
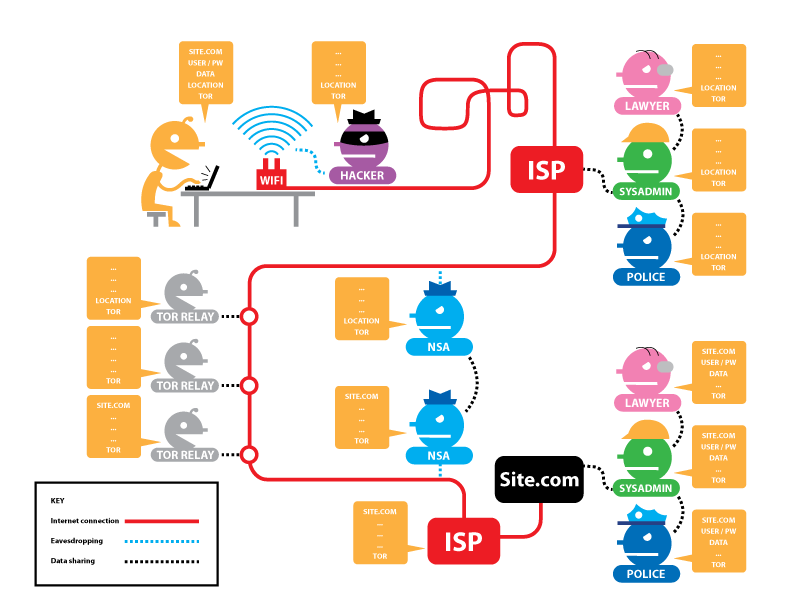
Now let's move on to the option when the Tor network is used and when a request is made to the site via HTTP (without using HTTPS encryption):
As you can see, your ISP knows your IP and knows that you use Tor, but does not know which sites you open and what data you send and receive.
The first Tor node knows your real IP and that you use Tor, but it knows nothing more about the requested and responded data.
The second Tor node never knows anything interesting at all.
But with the third Tor node, it’s more interesting: it does not know your IP, but it knows the data you transmit and even your login with a password. The same information is available to eavesdroppers in subsequent stages.
That is, the weaknesses of Tor:
- The Tor output node may be dishonest and collect data. But with all his desire, it cannot identify you. Although, if you use email as a login, then there are clues.
- Traffic from the Tor exit node to the website and vice versa is also unencrypted.
Fortunately, as already mentioned, there are not so many sites without HTTPS.
If Tor is used at the same time, and the site works via HTTPS, then the situation is as follows:
The main changes – the Tor output node and subsequent eavesdroppers can no longer access the transmitted data and user login/password. They know the site that was visited, but do not know by whom (your IP is hidden) and what data is sent and received (the traffic is additionally encrypted with an SSL certificate).
Pictures are taken from here: https://www.eff.org/pages/tor-and-https – on this page you can click interactive buttons and see what changes depending on a particular option.
The easiest way to use Tor
The easiest option to access the Internet through Tor is the Tor Browser – as mentioned at the very beginning, this is a special build of the Firefox web browser that includes Tor. When you start this browser, Tor starts at the same time, and then this browser only connects to the Internet through the Tor network.
Additionally, the web browser has plugins that prevent user tracking and promote anonymity.
In addition to plugins, the browser has settings, for example, not to save the browsing history and delete cookies after closing the site.
How to install Tor Browser on Windows
Download the self-extracting archive from the official site https://www.torproject.org/download/. Run it to unpack. Go to the directory created after unpacking and launch the Start Tor Browser shortcut. Click Connect and wait for the browser to connect to the Tor network.
If you want the sites to save the passwords you entered, then go to Preference, then Privacy & Security, uncheck ‘Always use private browsing mode’.
Restart your browser.
Go to Preference, then Privacy & Security and check the box ‘Ask to save logins and passwords for websites’.
How to install Tor Browser on Linux
First of all, look for the Tor Browser package in the standard repositories of your distribution.
In Kali Linux, install Tor Browser according to the manual on the page: https://miloserdov.org/?p=209
Services for finding IP address leaks
The main criteria for choosing a tool to ensure the anonymity of your operating system is the functionality and quality of ensuring anonymity (reliability of redirecting and blocking traffic). You can rate the level of anonymity using the following services:
- Identification of the use of anonymization tools: https://2ip.ru/privacy/
- Search for leaks of your IP or other data important for anonymity: https://whatleaks.com/
- Checking your IP, location and Internet service provider, there is support for IPv6 addresses: https://w-e-b.site/?act=myip
- Service for searching proxy headers and open ports, typical for anonymization tools: https://w-e-b.site/?act=proxy-checker
- Check if you use the Tor network: https://check.torproject.org/ (ATTENTION: be very careful with this service – it does not support IPv6. If traffic routing is not configured on your computer, this service will write that Tor is used, although all IPv6 traffic can go directly, revealing your IPv6 address!)
- Search for various leaks: http://www.doileak.com/
- DNS Leak Search: https://dnsleaktest.com/
- What every web browser knows about you: https://webkay.robinlinus.com/
- Checking of fingerprints that can be collected from your web browser: https://amiunique.org/fp
- View your User Agent: https://suip.biz/?act=my-user-agent
To check the IPv6 address on the command line and whether IPv6 protocol is blocked:
curl -6 suip.biz/ip/
To check your IP address on the command line:
curl suip.biz/ip/
To check the DNS server used:
dig suip.biz | grep SERVER
Related articles:
- How to redirect all traffic through the Tor network (100%)
- How to save and open website pages in Tails in a web browser (84.6%)
- Tor tips and usage examples (65.5%)
- Free easy way to hide IP in Linux (58.1%)
- How to install and run Tor Browser on Kali Linux (58.1%)
- How to see and change timestamps in Linux. How to perform timestamps-based searching (RANDOM - 50%)